Lambung
Hours 07.00 - 09.00
Hour picket flank organs are strong, it's breakfast for the establishment of the energy body throughout the day. Drinking juice or herb should before breakfast, so that the stomach is empty of useful substances soon be merged body.
Spleen
Hours 09.00 - 11.00
Hours picket strong organ spleen, in mentransportasi liquid nutrition for energy growth. When the hours this sleepy, it means the spleen is weak. Reduce consumption of sugar, fat, oil and animal protein.
Heart
Hours 11:00 - 13:00
Hours picket strong heart organ, must rest, avoid heat and physical manner, ambition and emotional disturbances, especially in people with blood vessel.
Heart
Hours 13:00 - 15:00
Hour picket organ weak heart, when people sleep, gather in the blood red heart and organ regeneration process occurs cells hearts. Strong function of the heart when the body strong to prevent any disease.
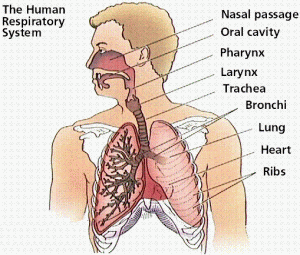
Lungs
Hours 15:00 - 17:00
Hour picket organ lungs weak, needed rest, sleep for the discharge of toxic and the process of the formation of energy consumption
Kidney
Hours 17:00 - 19:00
Hours picket strong organ kidney, should be used to study the process due to the formation of bone marrow and the brain and intellect.
Lambung
19.00 - 21.00
Hour picket organ weak stomach should not consume food which is difficult or long digested digested or better is to stop eating
Spleen
Hours 21:00 - 23:00
Hour picket organ spleen is weak, the process occurs and the discharge of toxic spleen cell regeneration process. Should rest while listening to music that calms the soul, to enhance immunity.
Heart
Hours 23:00 to 01:00
Hour picket organ weak heart. Bed rest should have been, if still working or begadang can weaken the heart function.
Heart
Hours 01.00 - 03.00
Hour picket organ heart strong. There was a process of toxic disposal / waste of body metabolism. If there is any interference in the function of heart reflected the dirt and disruption. If there is any injury will be felt in pain.
Lungs
Hours 03.00 - 05.00
Hour picket organ lungs strong, the process of waste disposal occurred / organ toxicity in the lungs, occurs when coughing, sneezing, sneezing and sweating indicates the existence of interference lung function. We recommend to use it to get a breath of energy tuberculosis healthy and strong.
Colon
Hours 05.00 - 07.00
Hours picket colon powerful organ, it is regularly biasakan CHAPTER
Versi Indonesia
Di bawah ini adalah sekilas tentang jam kerja organ tubuh kita dan ada sedikit deskripsi tentang apa yang sebaiknya kita lakukan pada jam-jam tersebut untuk menjaga kesehatan kita. Semoga dapat membantu.
LAMBUNG
Jam 07.00 - 09.00
Jam piket organ lambung sedang kuat, sebaiknya makan pagi untuk proses pembentukan energi tubuh sepanjang hari. Minum jus atau ramuan sebaiknya sebelum sarapan pagi, perut masih kosong sehingga zat yang berguna segera terserap tubuh.
LIMPA
Jam 09.00 - 11.00
Jam piket organ limpa kuat, dalam mentransportasi cairan nutrisi untuk energi pertumbuhan. Bila pada jam-jam ini mengantuk, berarti fungsi limpa lemah. Kurangi konsumsi gula, lemak, minyak dan protein hewani.
Jam 11.00 - 13.00
Jam piket organ jantung kuat, harus istirahat, hindari panas dan olah fisik, ambisi dan emosi terutama pada penderita gangguan pembuluh darah.
Jam 13.00 - 15.00
Jam piket organ hati lemah, bila orang tidur, darah merah berkumpul dalam organ hati dan terjadi proses regenerasi sel-sel hati. Apabila fungsi hati kuat maka tubuh kuat untuk menangkal semua penyakit.
Jam 15.00 - 17.00
Jam piket organ paru-paru lemah, diperlukan istirahat, tidur untuk proses pembuangan racun dan proses pembentukan energi paru-paru
Jam 17.00 - 19.00
Jam piket organ ginjal kuat, sebaiknya digunakan untuk belajar karena terjadi proses pembentukan sumsum tulang dan otak serta kecerdasan.
LAMBUNG
Jam 19.00 - 21.00
Jam piket organ lambung lemah sebaiknya tidak mengkonsumsi makan yang sulit dicerna atau lama dicerna atau lebih baik sudah berhenti makan
Jam 21.00 - 23.00
Jam piket organ limpa lemah, terjadi proses pembuangan racun dan proses regenerasi sel limpa. Sebaiknya istirahat sambil mendengarkan musik yang menenangkan jiwa, untuk meningkatkan imunitas.
Jam 23.00 - 01.00
Jam piket organ jantung lemah. Sebaiknya sudah beristirahat tidur, apabila masih terus bekerja atau begadang dapat melemahkan fungsi jantung.
Jam 01.00 - 03.00
Jam piket organ hati kuat. Terjadi proses pembuangan racun/limbah hasil metabolisme tubuh. Apabila ada gangguan fungsi hati tercermin pada kotoran dan gangguan mata. Apabila ada luka dalam akan terasa nyeri.
Jam 03.00 - 05.00
Jam piket organ paru-paru kuat, terjadi proses pembuangan limbah/racun pada organ paru-paru, apabila terjadi batuk, bersin-bersin dan berkeringat menandakan adanya gangguan fungsi paru-paru. Sebaiknya digunakan untuk olah nafas untuk mendapatkan energi paru yang sehat dan kuat.
Jam 05.00 - 07.00
Jam piket organ usus besar kuat, sebaiknya biasakan BAB secara teratur